Wholesale orders
4 minute read
What you’ll learn
- What is wholesale pricing
- Data model review
- How to create orders with when the wholesale pricing model is used
Wholesale pricing
Traditionally, Marketplacer has focused on a Business to Consumer (B2C) model, where products are offered for sale to retail consumers. By also allowing products to be priced using a wholesale pricing model, products can be offered for sale to other businesses using the Business to Business Model (B2B).
The key characteristics of wholesales prices are:
- Lower than Retail Prices: This is the most fundamental characteristic. Wholesale prices are set significantly lower per unit than retail prices to allow for associated (upward) adjustments.
- Bulk Purchase Requirement: Wholesale transactions almost always involve buying goods in large quantities, often with minimum order quantities (MOQs). This volume allows the seller to achieve economies of scale and offer the discounted price.
- Business-to-Business (B2B) Focus: Wholesale pricing is primarily for transactions between businesses, such as a manufacturer selling to a retailer, or a distributor selling to a smaller business for resale.
- Exclusion of Sales Tax (typically): Since wholesale transactions are part of the supply chain and not direct sales to the final consumer, sales tax is generally not applied at the wholesale level.
The remainder of this article focuses on creating orders in Marketplacer when wholesale pricing has been adopted for some or all of the products hosted on Marketplacer.
Wholesale Pricing Availability
Wholesale pricing is currently only available in AU/NZ.Model Review
Order model
The following model is discussed in more detail in the main Creating Orders article, but it’s worth recapping here:
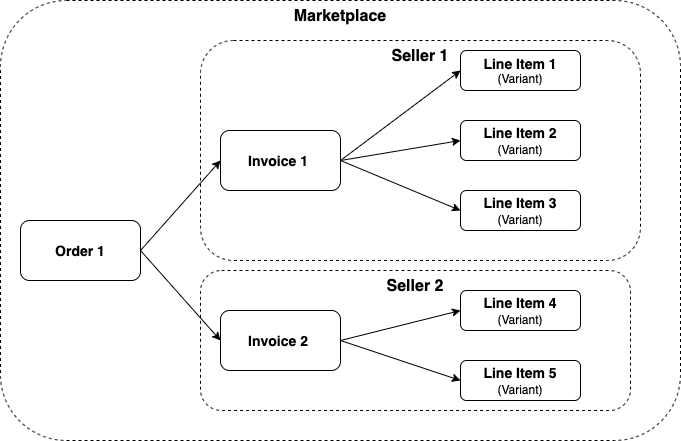
The key takeaways are:
- An order is a marketplace-level object, that contains 1 or more invoices
- An invoice is a sellers view of the order
- Invoices (and by extensions orders) have 1 or more line items
- Line items have a line of sight back to the product variant
Product model
When talking about products in Marketplacer, we’re really talking about 2 related entities:
- Adverts (aka Products)
- Variants
The following model describes the relationship between the 2:
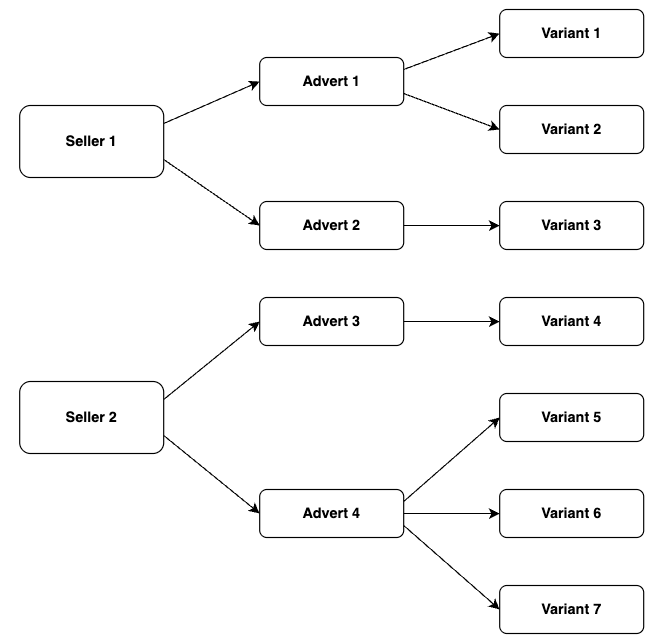
Key takeaways are:
- Adverts act as the product container for variants
- An advert must have at least 1 variant
- Variants are the container for the following fields:
- Stock position (called
countOnHandin Markertplacer) - Barcode
- Sku
- Pricing Model (Marketplace or Wholesale)
- Stock position (called
- It is the variant that is purchased (and used when creating an order)
- As mentioned above, the Pricing Model is set at the variant level
- A seller can sell variants that use either of the following pricing models:
- Marketplace
- Wholesale
- An Advert have variants that use either of the following pricing models:
- Marketplace
- Wholesale
To illustrate how different pricing models can be adopted, we have updated the product model diagram as follows:
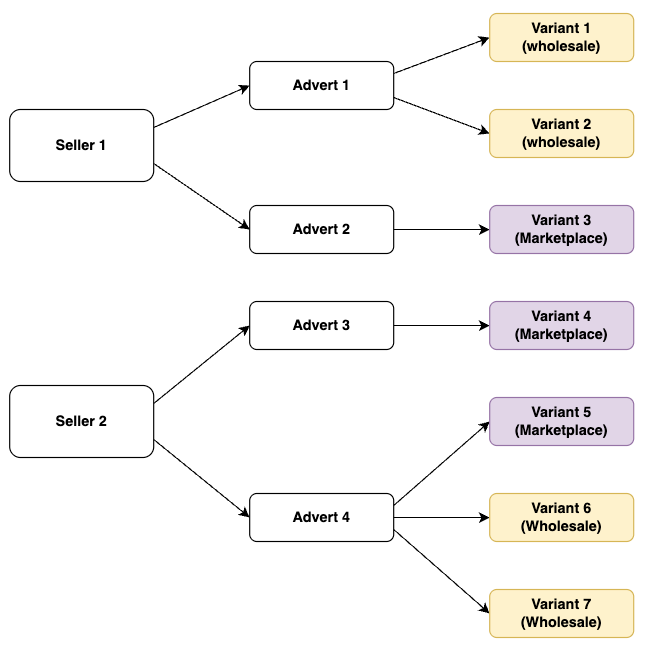
Creating wholesale orders
Creating orders with wholesale variants is no different to creating any other type of order - as described here.
However, when it comes to creating orders where there is a mix of pricing models, the following rules apply:
| Scenario | Seller 1 Line Items | Seller 2 Line Items | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Seller: -Seller 1: Marketplace pricing | - Marketplace pricing | N/a | Order Created |
| 1 Seller: -Seller 1: Wholesale pricing | - Wholesale pricing | N/a | Order Created |
| 2 Sellers: -Seller 1: Marketplace pricing -Seller 2: Wholesale pricing | - Marketplace pricing | - Wholesale pricing | Order Created |
| 1 Seller (mixed pricing): -Seller 1: Marketplace pricing -Seller 1: Wholesale pricing | - Marketplace pricing - Wholesale pricing | N/a | *Order not created |
In short the same seller cannot have both Marketplace and Wholesale priced variants on the same order.
For an example of the error that would be returned in this case please refer to theorderCreatereference guide.
Example - Mixed Pricing / Different Sellers
To round out the conversation, below you can find an example of orderCreate where we are using mixed pricing models for 2 different sellers (which is permitted):
- Variant 1 (
variantId:VmFyaWFudC01MzU2) is a wholesale priced variant for Seller 1 - Variant 2 (
variantId:VmFyaWFudC01MzU0) is a marketplace priced variant for Seller 2
Note: The
costamount supplied for both line items should be the retail cost charged to the end customer, even when wholesale pricing is being used.
This will result in:
- The successful creation of 1
order- The creation of 1
invoicefor Seller 1 (Wholesale pricing used) - The creation of 1
invoicefor Seller 2 (Marketplace / Retail pricing used)
- The creation of 1
mutation {
orderCreate(
input: {
order: {
firstName: "Trisha"
surname: "Connors"
phone: "07944242424"
emailAddress: "trisha.connors@email.com"
address: {
address: "34 Casino Road"
city: "Melbourne"
country: { code: "AU" }
postcode: "3000"
state: { name: "Victoria" }
}
}
lineItems: [
{
# Seller 1: Wholesale priced variant
variantId: "VmFyaWFudC01MzU2",
# Even though this is a Wholesale priced vatiant
# the cost vaule supplied should be the retail price
cost: { amount: 1000 },
quantity: 1
}
{
# Seller 2: Marketplace priced variant
variantId: "VmFyaWFudC01MzU0",
cost: { amount: 1000 },
quantity: 1
}
]
}
) {
order {
legacyId
invoices {
nodes {
id
legacyId
seller {
businessName
}
lineItems {
id
}
}
}
}
errors {
field
messages
}
}
}